By DAVID L. HEISERMAN
(Electronics World, Nov. 1971)
Various types of electronic image-intensifier tubes are used in astronomy for light-intensity measurements and other photometric studies. Here are descriptions of several kinds and how they operate.

ABOVE: Image-tube photo of the Dumbell Nebula made by R.E. Williams
at University of Arizona's Steward Observatory.
ONE of the main goals of modern technology is to develop instruments that extend the range of normal human senses. The human eye, for example, doesn't function very well in a darkened environment. Technology has answered this particular challenge with several kinds of see in-the-dark devices, including electronic images tubes.
Commercial electronic image tubes--or image--intensifier tubes to be more precise -accept light from a dimly lit scene, amplify it electronically, and produce a brightened version of the original scene on a phosphor viewing screen.
Unlike ordinary TV camera tubes, image tubes produce their output images simply and directly without resorting to electronic scanning.
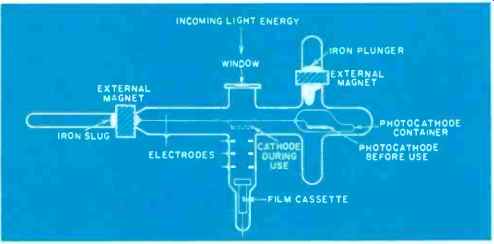
Fig. 1. Although Lallemand tubes, properly called "electronic cameras," are
extremely awkward to set up and use, astronomers have applied them quite
successfully since the 1930's.
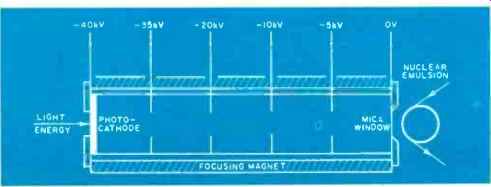
Fig. 2. Because they are so easy to set up and operate, Spectracon tubes
are most promising astronomical image devices.
Astronomers have always been interested in getting brighter views of the objects they study through their telescopes, so it was inevitable that image tubes would find their way into observatories. It was an astronomer, in fact, who built the first workable electronic image-intensifier just prior to World War II. The device, called a Lallemand tube or camera, produces its output images on a piece of film rather than on a directly viewable phosphor screen. As far as astronomers are concerned, film is still the best image -tube output medium. When industry and the military took up image -tube development during World War II, however, the film was eliminated and phosphor screens took over.
Most people who buy image tubes today are interested in one thing--seeing in the dark. Whether or not the contrast is perfect is of no real concern as long as they can see what they want to be able to see. Astronomers, on the other hand, must be able to make reliable measurements of the relative light intensities and perform other kinds of photometric studies that demand faithful reproductions of the original contrast information.
Commercial image tubes have directly viewable phosphor screen outputs and, in order to make photographs of the images, astronomers have to use a light-sensitive film.
However, films that have sensitivities and spectral responses matching light from phosphor screens do not reproduce contrast information linearly. Light-sensitive emulsions have intensity response curves that level off at some saturation point. The more exposed a portion of the film becomes, the smaller the effect each photon has upon it.
Astronomers use an electron-sensitive film, called a nuclear emulsion. By discarding the phosphor screen and replacing it with a nuclear emulsion, every electron from the photocathode contributes exactly the same amount of exposure, no matter how much activity has gone on before. Astronomers, in other words, want a linear contrast response that a phosphor -film interface on an image tube cannot provide.
In spite of astronomers' needs, the development of commercial phosphor-screen image tubes proceeded quite rapidly. Among the more popular image -tube devices are the infrared "snooperscopes" of WW II and the starlight scope now used in Vietnam. The military market for image tubes has grown to the point where it is possible to buy new tubes for less than $1000 and surplus tubes for less than $300. Compared to these commercial and military devices, the image tubes astronomers have to beg, borrow, or build seem primitive. Some astronomers can buy new astronomical image tubes that are custom products from major image-tube manufacturers, but the small demand keeps the price in excess of $25,000 per unit!
Lallemand Tubes
Although Lallemand tubes are simple in principle, they are extremely awkward devices to prepare and use. A specialist has to begin preparations at least a day in advance and, even then, he has to prepare several tubes at a time in case something goes wrong with one or two of them. The most delicate part is the photocathode. These elements arrive at the observatory sealed in evacuated glass vials. The vials protect the cathodes from both physical damage and contamination by moisture and chemicals in the air.
When preparing a Lallemand tube, the user has to load the film cassette and photocathode--still in its glass container -into the tube through a small window opening (Fig. 1). The entire photocathode assembly remains in a position well away from the film until the moment the tube is ready for use. After loading the tube and sealing the glass window into place, the user must evacuate the tube and bake it out as much as possible without damaging the emulsion.
When the tube is in place on the telescope and the astronomer is ready to expose the film, he has to break the glass container around the photocathode by hammering it with a magnetically operated iron plunger. He then uses another magnet to pull the bare cathode into place over the film cassette. If all goes well to this point, the only remaining step is to slide the cover off the film cassette with another external magnet. The cassette has several plates in it that the user can change, also by means of an external magnet.
When he uses up all the plates in the film cassette, the astronomer has to break the vacuum on the tube and remove the exposed plates through the opened window.
Breaking the vacuum exposes the photocathode to contamination, however, so the tube must be completely disassembled and prepared for use again.
Kron Tubes
C.E. Kron, an astronomer at Lick Observatory ( California), decided that contamination of the photocathode created most of the headaches associated with Lallemand tubes.
He built a modified Lallemand tube that has a vacuum seal between the cathode and film cassette. Once the cathode is in place, it can be sealed off from the rest of the tube whenever the user wants to change film cassettes. After changing the film, the user reseals the opened half of the tube, evacuates it, and opens the vacuum seal.
The photocathode in a Kron tube, unfortunately, doesn't last indefinitely, either. Electrons striking the nuclear emulsion send off energetic bits of matter and ions that contaminate the photocathode material. This contamination eventually builds up to a point where the user has to replace the cathode.
The Kron tube is now a popular device among image tube astronomers. Although it reduces the preparation time considerably, a Kron tube still requires a skilled operator to manipulate the magnetic cassette mechanism, operate the vacuum system, and occasionally change the photocathode.
Spectracon Tubes
The most promising astronomical image tube in use and still under further development is one designed by J.D. McGee at the Imperial College in London. Contrary to popular consensus, McGee decided to bypass all the problems with the Lallemand and Kron tubes by placing the nuclear emulsion outside the tube.
McGee's astronomical image tube, called a Spectracon, contains the photocathode and accelerating electrodes in a permanently sealed glass envelope (Fig. 2). A small mica window, only about 4 microns thick, transmits energetic electrons out of the tube to the nuclear emulsion. This technique reduces the quantum efficiency of the tube by about one -third, but it eliminates all forms of cathode contamination, and does away with all the tricky magnet manipulations and vacuum processes.
The Spectracon doesn't require a highly skilled operator and it can be set up and in full operation within minutes.
Astronomers are now beginning to believe these two advantages alone compensate for the loss of quantum efficiency.
The current activity in Spectracon development concerns finding materials that make it possible to build tubes with larger output windows. Since the windows have to withstand full atmospheric pressure, the largest Spectracon windows measure only 4.5 by 33 mm. This long and narrow configuration makes it almost impossible to take electrographic pictures of large stellar objects. For this reason, astronomers generally use Spectracons only for analyzing the spectral content of steiler light.
Merle F. Walker, one of America's leading image-tube astronomers, recently stated that "The one-million-dollar cost of developing the 4-inch diameter (image) tube is less than that of a single new telescope 100 inches or more in aperture, but the results for photometry would be to transform every existing 60 -inch instrument (telescope) into a 200-inch!"
ABOVE: Image-tube photo of Smoke-Ring Nebula from Steward Observatory.
Also see: