AMAZON multi-meters discounts AMAZON oscilloscope discounts
Most PCB (printed-circuit board) issues can be traced to non-continuous signal return paths. Today, this is more of an issue due to increasing clock frequencies.
AMAZON multi-meters discounts AMAZON oscilloscope discounts
Solutions:
- Best if the signal travels out a trace and returns immediately under that trace
- Unfortunately, the return path is often broken by a discontinuity: e.g. a gap or slot in the ground plane or the signal trace passes through a via and changes reference planes
- Carefully examine ground (and power) plane layers for gaps and slots
- Add extra vias for return currents when switching reference planes
Production of differential-mode emissions
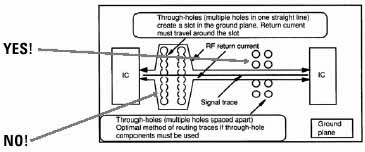
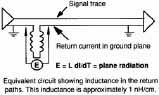
Above:
Ground loops when using through-hole components.
Differential Mode current flows in a loop. The loop radiates energy.
Examples of Non-continuous Return Paths
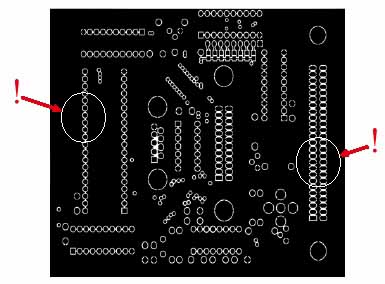
Slots in data-acquisition board signal return plane
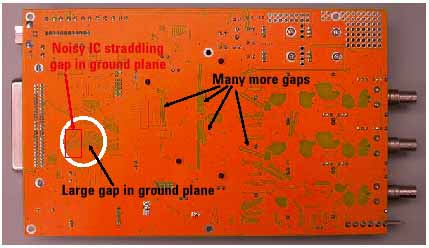
Above image shows:
- Noisy IC straddling gap in ground plane
- Huge gap in ground plane
- Several more gaps
A temporary bridge with copper tape is used to reduce emissions by as much as 20 dB.
Non-continuous Return Paths (examples)
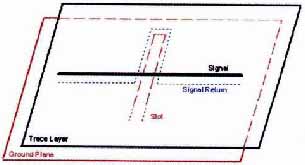
Above: Routing a trace over a slot in a plane can cause a large loop area.
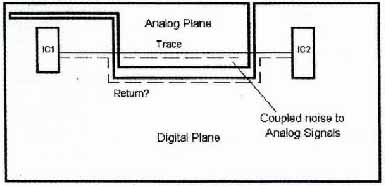
Above: Routing a trace over an unrelated plane can cause several types of
problems.
Trace passing through two planes with via
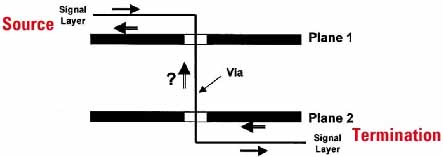
Above: Source / Termination. Signal Traces Adjacent to Different Planes. But ... where does the return signal current flow?
| EMC Top Ten: 8 | EMC Top Ten: 10 |