AMAZON multi-meters discounts AMAZON oscilloscope discounts
When it comes to environmental test chambers, humidity can be a confusing topic. Part of the confusion is due to the fact that relative humidity (RH) is temperature-specific. For example, the amount of moisture in the air at 10-degrees Celsius and 50% RH is not equivalent to the amount of moisture in the air at 20-degrees Celsius and 50% RH. As air temperature increases, the air's capacity to hold moisture also increases.
Most chambers have a temperature/humidity range of 7-degrees Celsius to 85-degrees Celsius with 10% to 98% RH, limited by a 5-degrees Celsius dew point. The 5-degrees Celsius dew-point limitation is a bit confusing. Let's try to clarify this...
Because the amount of moisture varies at every temperature, chamber manufacturers use dew point to describe the RH limitation. Inside the chamber, there is a refrigerated coil controlled at or slightly below 5-degrees Celsius moisture in the chamber. Moisture will condense on the cold surface. The water that accumulates is drained out of the chamber, lowering the RH. The refrigerated coil is never below freezing (0-degrees Celsius) so there are no frost problems.
The simplest way to understand this is to look at the performance curve below:
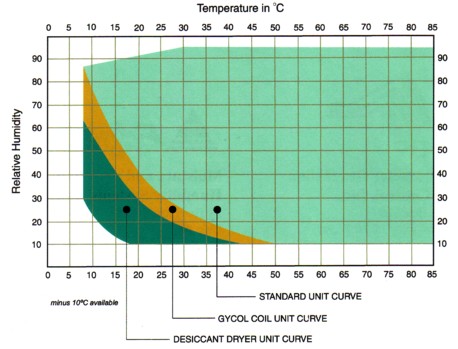
If you follow the lower edge of the Standard Unit Curve (where light green area meets beige area), those temperatures and humidities represent the 5-degrees Celsius dew point. For example, the lowest humidity level achievable at 35-degrees Celsius is 25% RH. At 50-degrees Celsius, it's 10% RH. It must be operated within the limits set by the manufacturer; damage to the refrigeration system can occur if operated outside the standard range.
To achieve even lower humidity levels, several manufacturers offer a low-RH package (the examples on this page don't offer this). It usually includes a dry-air purge system and refrigeration valves to allow the refrigerated coil go below freezing. This is accomplished when the dry-air purge and frozen-coil are activated. There is a potential for the coil to accumulate frost at these conditions. But, the dry-air purge helps to offset this by keeping a positive pressure in the chamber and sublimating some of the accumulating frost off the coil.
Example of a typical Humidity-Control Environmental Test Chamber:
 above: A 30 Cubic Foot Unit Humidity-Control Test Chamber from PGC |
Specifications Utilities * Electrical: 230 volts, 1 phase, 50/60 Hz, (15 fla) Dimensions RH Variables Control Constancy ± 0.5% Chamber Uniformity ± 0.5% Sensor Accuracy ± 1.0% Total ± 2.0% Description: The PGC 30 cu. ft. chamber, above, features a unique humidity control system that enables the user to attain unsurpassed levels of relative humidity/temperature control and uniformity. These test chambers are designed to accurately produce those temperature and humidity conditions required for applications such as stability studies, package testing, TAPPI, MIL-SPEC, and vapor transmission. Applications are found in such diverse industries as pharmaceutical development and manufacturing, electronic components, food, semiconductor, paper and pulp, and wherever precise humidity and temperature replications are required. Additionally, PGC's SmartPad microprocessor controller is a user-friendly system that provides optimum accuracy and control. The SmartPad is equipped with direct readings in both temperature and humidity. It also features 60-segment programming for automatic cycling and ramping and soaking excursions. High-low or deviation alarms as well as digital communications ports are standard features. The interior chamber is constructed of very durable, corrosion resistant 316 stainless steel. Low watt density heaters are used that also contribute to the unit's longer life. Should your application require it, the chamber air flow can be factory-configured from the standard horizontal flow to vertical. Other options include extended ranges, chart recorders, a window in the outer door, and a clean inner door with optional iris opening.
|
Uses for Temperature/Humidity ranges in Environmental Test Chambers
- Humidity cycling and temperature-humidity cycling
are used to assess the effect of swelling from moisture absorption on
product reliability. The cyclic nature of these tests accelerates damage
accumulation from periodic moisture absorption and desorption during
changes in environmental humidity.
- The temperature-humidity-bias (THB) test is used to test for moisture-induced failures. The test requires the devices to undergo a constant temperature, elevated relative humidity, and electrical bias (constant or intermittent, based on device type). Voltage cycling may be required to prevent the device from heating up and preventing moisture effects from occurring.
NEXT: Temperature Change Rate