AMAZON multi-meters discounts AMAZON oscilloscope discounts
The graph below can be used to find the static deflection for isolators that's required to provide a given degree of isolation from vibrating equipment. For example, in a gymnasium (“noncritical” application) an exhaust air fan operating at a driving frequency of 520 rpm will require resilient isolators which have a static deflection of at least 1 in (see dashed lines on graph).
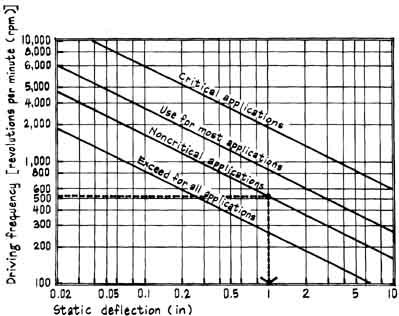
The relationships depicted on the graph are for resilient materials sup ported by a rigid structural base or foundation. Non-rigid, lightweight bases (especially lightweight steel or wood frame flooring systems) used for above- grade mechanical equipment spaces require greater isolation deflections than given by the graph. Lightweight bases are less stiff and therefore require greater isolator deflections. Special care must be taken when designing vibration isolation for these situations.
Next: Rubber Mounts