The decimal system of numbering, counting, and performing mathematical operations is the best-known number system.
Thus, it usually serves as a reference for other systems. The decimal system up to number 33 is shown in column 1 of Table B-1 . The equivalents in natural binary are shown in column 3. Thus, decimal 4 represents the same quantity of things as binary 000100. Column 4 shows the excess-3 binary number code. The system throws away the first 3 counts of natural binary and starts at binary 000011, which is actually the fourth count in straight binary. Thus, 000011 in Excess-3 binary is the equivalent of decimal 0. Column 5 shows the "2-out-of-5" numbering code. This code uses 5 bits but uses only those combinations which have two is and three 0s. This code is useful in certain types of mathematical operations.
Column 6 shows binary coded decimal. Each digit requires 4 bits. Thus, 0111 is the equivalent of decimal 7, and 1000 is the equivalent of 8. To write a two-decimal-digit number re quires two binary-coded-decimal groups of 4 bits each. Thus, number 12 is written as 0001 followed by 0010, which is the equivalent of 1 and 2 respectively.
The octal system, Column 7, uses only 3 bits; therefore, it can represent only 8 levels-0 through 7. The next quantity after 7 is 8, which is written as 001 followed by 000. This is written in the octal ( base 8) system as 10 and is the equivalent in decimal of 8. The octal system fully utilizes its 3-bit identification scheme, whereas the binary-coded decimal system uses only 10 different codes of the 16 possible with a 4-bit word.
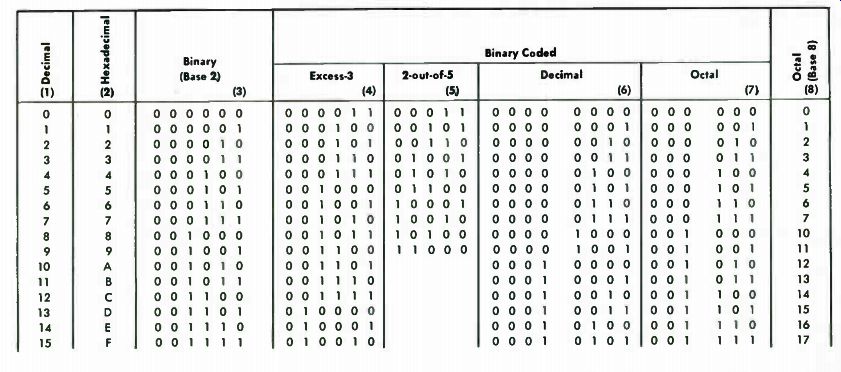
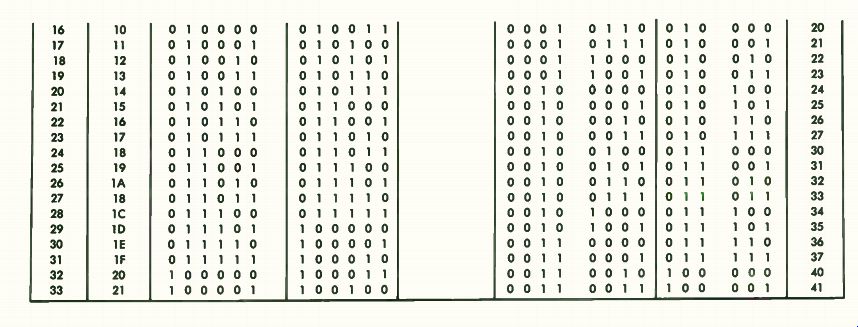
To take full advantage of the 4-bit code, the hexadecimal numbering system ( Column 2) was developed. Since only 10 different numerals are available, the letters A, B, C, D, E, and F have been used to give single character representation for 16 different levels or quantities. At level 16, two hexadecimal characters are required. Number 16 is written as 10, while 1F is the equivalent of decimal 31.
Prev: DIGITAL LOGIC CONVENTIONS
Next: TTL POWER SUPPLY
Guide Index : Transistor-Transistor Logic (early 1970s)